Our Products
CETP- Common Effluent Treatment Plant
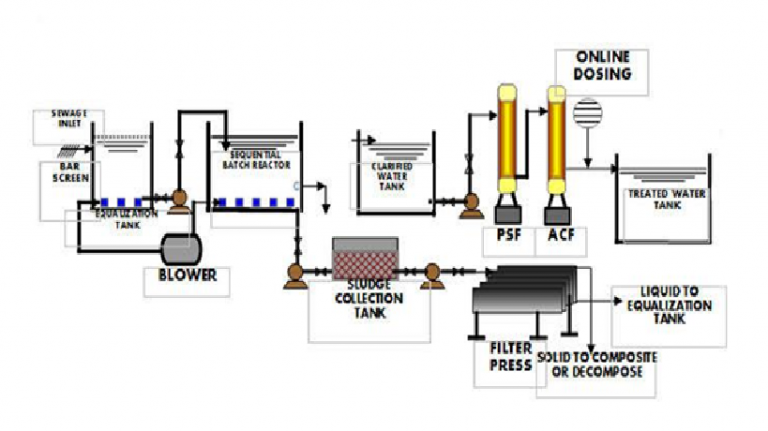
CETP -COMMON EFFLUENT TREATMENT PLANT
Common effluent treatment plants (CETPs) have been installed and are in operation at numerous industrial clusters throughout India. They serve to reduce effluent treatment cost, provide better collective treatment, and reduce land cost for small-scale industrial facilities that cannot afford individual treatment plants. Optimum working conditions for treatment of effluent to be at par with discharge standards is a major mandate for any CETP.
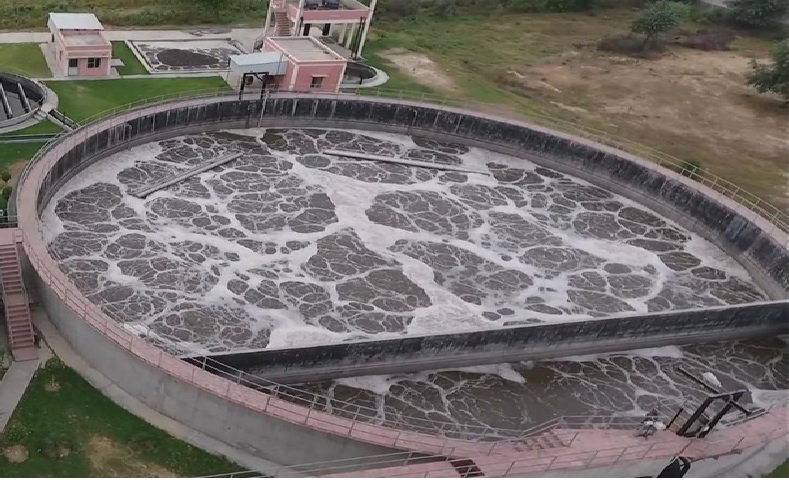

Aeration
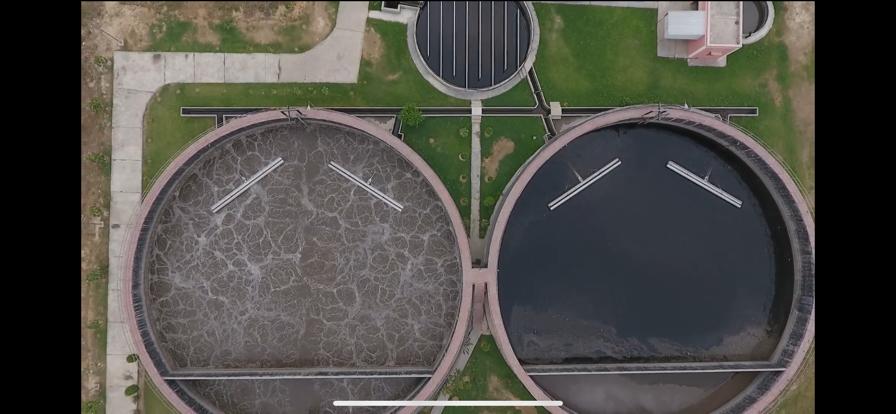

Sequential Batch Reactor
An established methodology is adopted to determine the effectiveness of the CETP in terms of biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), and oil and grease (O&G) concentrations. The CETP’s compliance with respect to design standards and its operation were studied in detail. This paper highlights the results of RE and the coefficient of determination (R2) values obtained from the CETP data, estimates the pollutants removed at the highest and lowest rates over a period of time, and highlights the reasons for problem areas along with remedial measures.
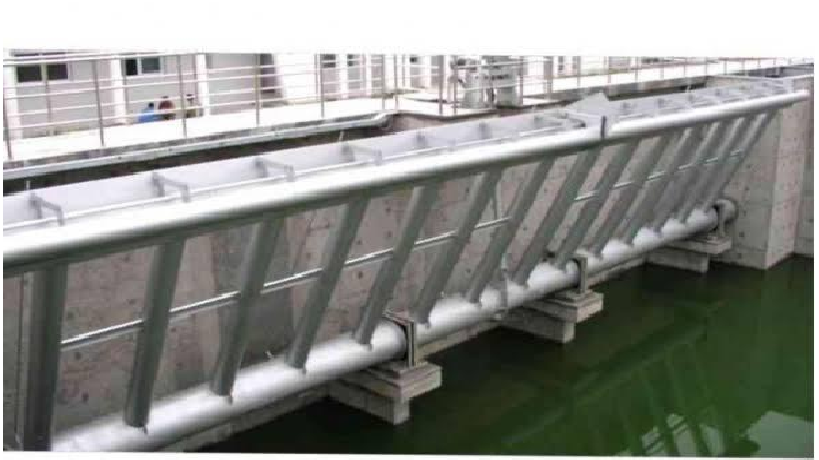

ERECTION OF MECHANICAL DECANTERS
STP - Sewage Treatment Plant

SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT ON SBR TECHNOLOGY
SBR is a high-performance solution for wastewater treatment that can successfully handle batch and continuous flow operations. It is a proven technology with minimal costs and maintenance requirements. Due to high removal capacity and versatility, it is compliant with stringent discharge standards. Biological process and high-quality product generation are the distinct qualities of SBR based sewage treatment plant.
Due to streamlined design, Water Wings designed Sewage Treatment Plant is one of the most favored wastewater treatment systems today. This highly flexible technology is useful in a wide variety of applications.
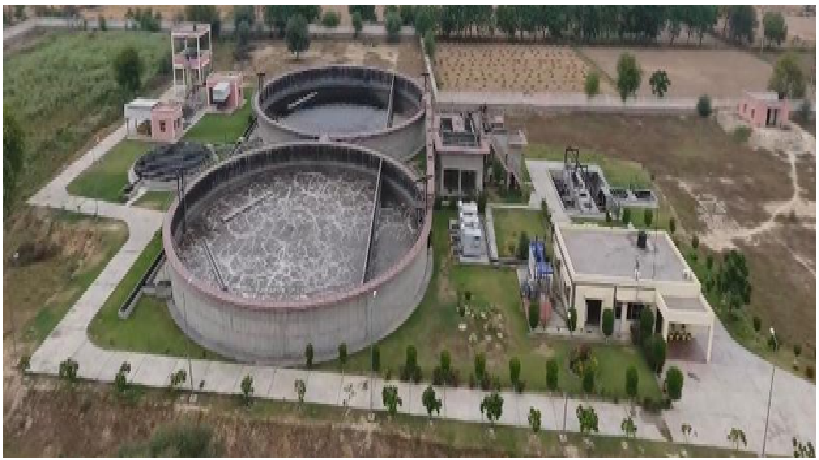


Water Treatment Plants
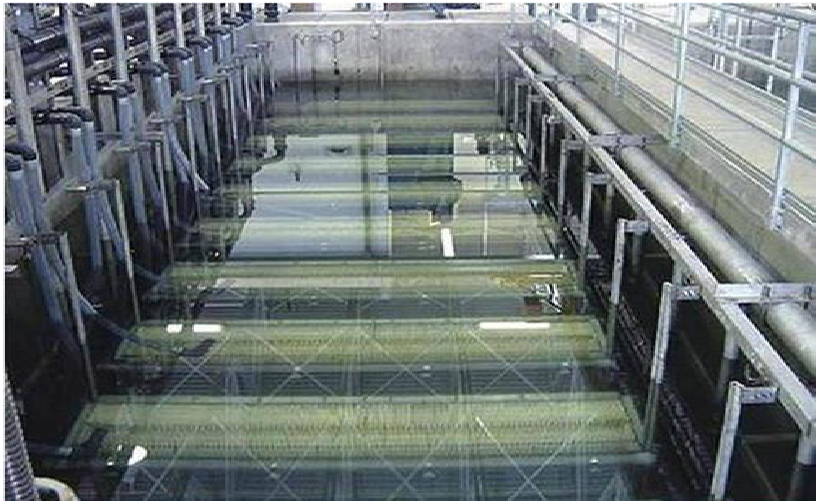
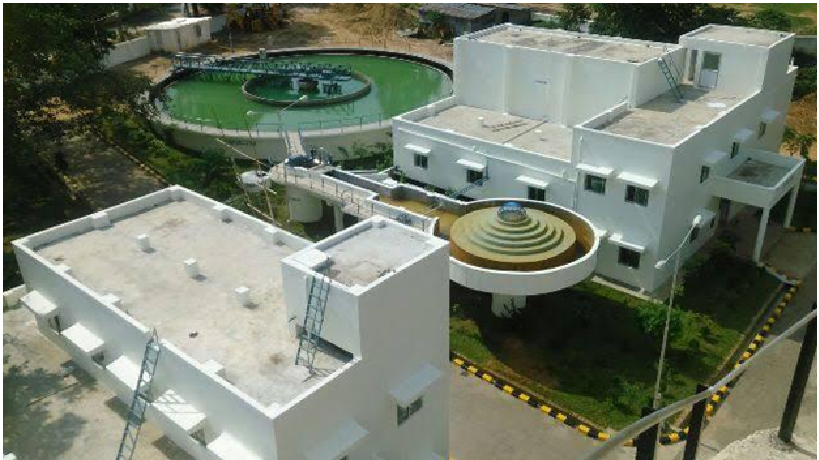
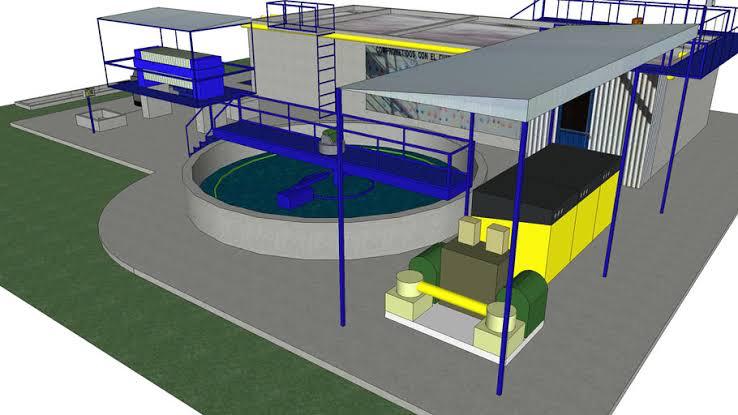




Urbanisation and industrialisation has led to an enormous increase in the waste water from both domestic setups (Sewage Treatment Plants) and industries (Effluent Treatment Plants). Waste water must be treated because about 80% of it flows unfiltered into lakes, rivers, seas and oceans and this leads to environmental hazards. It causes build up of organic and in-organic contaminants, heavy metals and pathogens in these water bodies which harm the aquatic ecosystem. Treatment processes, prior to disposal is a must in order to prevent the contaminants from entering the water and this make the water less harmful to the environment. With new integrated technologies and comprehensive service, Water Wings, a leading industrial water and waste water company, complete solutions for a clean and future-ready water industry. Water Wings is the distributor of sewage treatment plants and effluent treatment plants pan India and we also install sewage and effluent treatment plants. We also assist with the construction of Sewage treatment plant.
The advanced treatment processes from Water Wings remove pathogens, organic waste, oils, toxic chemicals and heavy metals from the water and are energy-efficient and stand up to the standards. Stepwise process is adopted to treat the water and the process varies depending on the nature of waste accumulated in the water.


Membrane bioreactor (MBR) is the combination of a membrane process like microfiltration or ultrafiltration with a biological wastewater treatment process, the activated sludge process, now widely used for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment
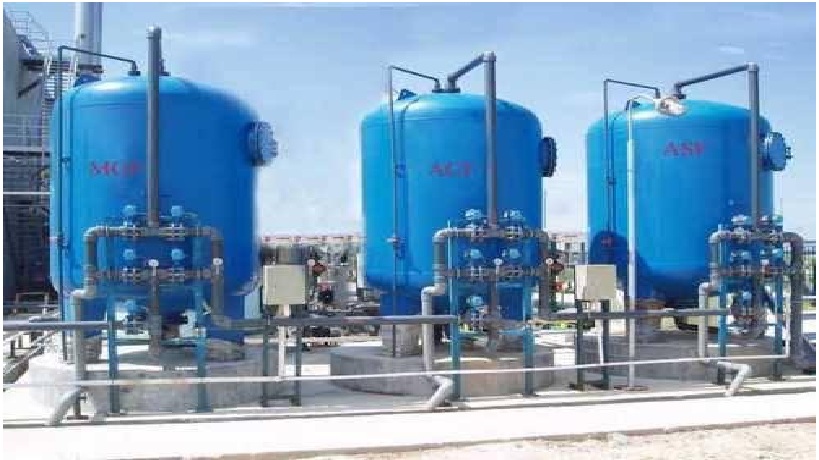
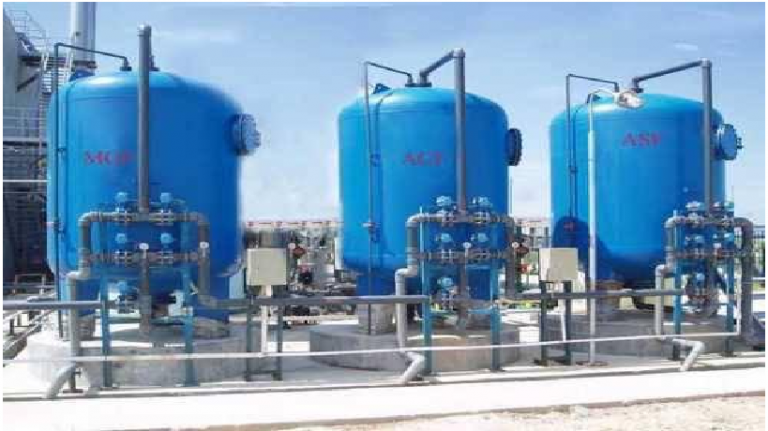
PRESSURIZED SAND FILTER (PSF), DUAL MEDIA FILTER (DMF), and ACTIVATED CARBON FILTER (ACF) and DISINFECTION UNIT. This treatment consists in removing taste, odor and organic load left after secondary treatment (killing of pathogenic Bacteria).

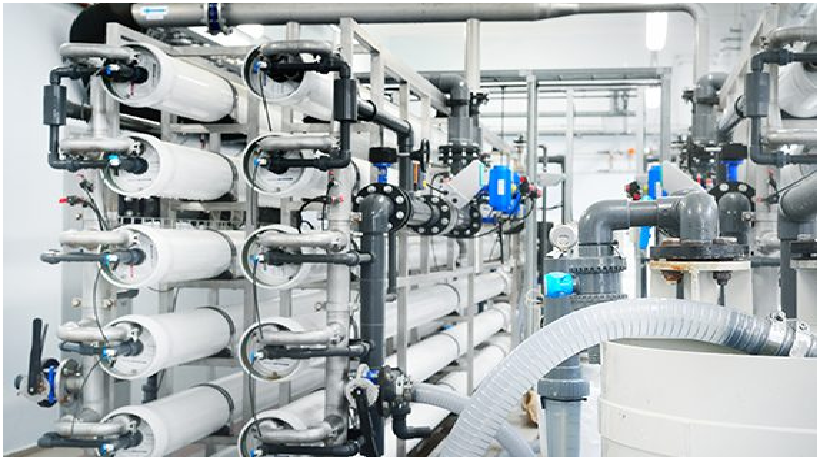
Commercial Reverse Osmosis Plants
If you’re looking for a water treatment system that provides outstanding quality of drinking water for your industrial use, Water Wings’s Commercial Reverse Osmosis (RO) system is one of the most popular and the best water filtration methods available. It removes dissolved impurities from water using a membrane that filters particles and only let’s water to pass through.
Various types of contamination of wastewater require a variety of strategies to remove the contamination. Industrial Reverse Osmosis (RO) units use high-efficiency reverse osmosis membranes that are designed to produce low dissolved solids from running water or stagnant water.
Designed to suit the client’s needs and made out of quality and durable materials, Water Wings’s water treatment and wastewater treatment equipment ensure to optimize the water treatment process. We are one of the best reverse osmosis suppliers in pan India.

Water Softners
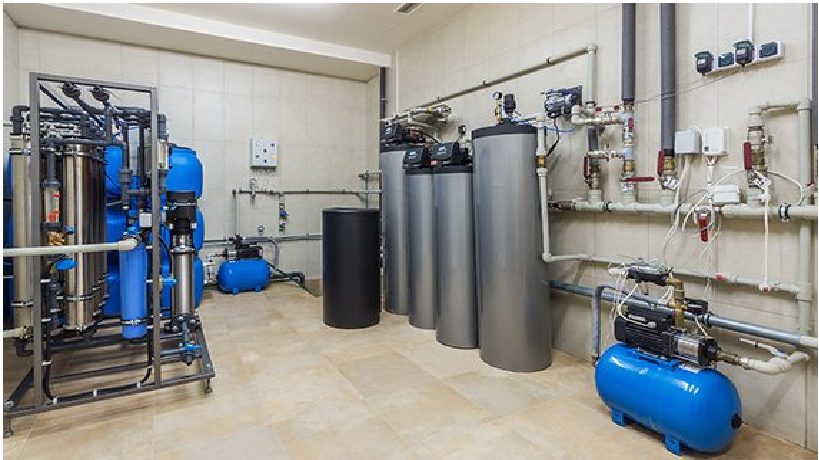

Water softening is the removal of calcium, magnesium, and certain other metal cations in hard water. The presence of certain metal ions like calcium and magnesium principally as bicarbonates, chlorides, and sulfates in water causes a variety of problems. Hard water leads to the build-up of lime scale, which can foul plumbing, and promote galvanic corrosion. In industrial scale water softening plants, the effluent flow from the re-generation process can precipitate scale that can interfere with sewage systems.
Extensive range of Water softeners offered by Water Wings will ensure that your homes and offices receive soft and clean water irrespective of the amount of hardness in your raw water. Water Wings is one of the best Water softener suppliers in pan India.
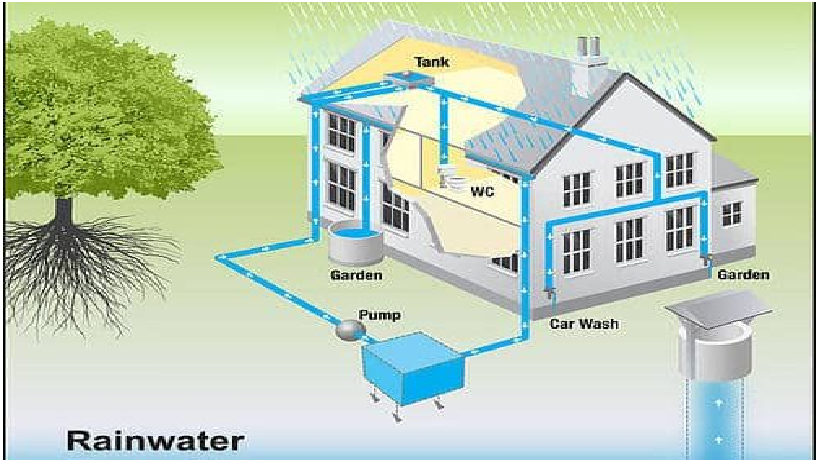
Rain Water Harvesting (RWH) System
With the growing need of stepping towards highly operative water preservation & conservation techniques, Rainwater Harvesting stands ahead. The process of harvesting rainwater differs for industrial and domestic purposes. Rainwater harvesting provides independent water supply during regional water restrictions for example when drought occurs and can reduce water demand on wells, sustain groundwater levels by refilling it with rain water and reuse of the treated rain water. It also helps in the availability of potable water, as rainwater is substantially free of salinity and other salts. Water Wings always stands atop in transforming the future of water by assisting every step towards water conservation that’s very much evident from the cost-effective designs of the Rain Water Harvesting (RWH) Plants in accordance to the your requirement. Water Wings designs and installs Rain Water Harvesting (RWH) systems that suit the exterior of your house there by making it more appealing.
What is Waste Water?
What is Waste Water?
It is used water originating from domestic, industrial, agricultural and medical activities. Upon usage, the quality and composition of the water changes deeming it unfit for further use.
However, the water released from ponds or reservoirs, used for fish farming, is not considered as wastewater.
Types of Waste Water
Domestic Waste Water is all the water used in domestic dwellings (e.g. originating from small trades, schools, private households, and public authorities). Wastewater from domestic dwellings is quite similar in composition (with regard to the substances in the wastewater). Wastewater from hospitals might be of higher concern though, because of the pathogens and medical contaminants it might contain.
Industrial Waste Water is the water that has been used as part of making a commercial product and has a different chemical composition to domestic Waste Water. Whether it’s the food we eat, the beverages we drink, the clothes we wear, or the paper and chemical products we use, water is required for nearly every step of production across a multitude of different industries. The resulting wastewater must be carefully managed. Regardless of how wastewater is treated, the “end product” is called effluent. To comply with environmental protection laws, certain contaminants must be removed from the wastewater. This includes organic matter, inorganics (sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, copper, lead, nickel, and zinc), pathogens, and nutrients (most notably nitrogen and phosphorus).
Storm (Rain) Water is the water that originates from precipitation, including snow and ice melt. With less vegetation and more impervious surfaces (parking lots, roads, buildings and compacted soil), developed areas allow less rain to infiltrate into the ground, and more runoff is generated than in the undeveloped condition. Additionally, conveyances such as ditches and storm sewers quickly transport runoff away from commercial and residential areas, carrying along with pollutants like sediments, nutrients, bacteria, pesticides, metals, and petroleum byproducts, into nearby sewers.
Extraneous Water is the unpolluted groundwater and spring water which enter the sewer system due to leakages or due to cross-connections. Roughly 20% of treated wastewater is extraneous water, in some cases, wastewater may increase the fourfold and more.
Agricultural Water Waste is the water from agricultural activities (fertilizers and manure) and stables (animal urine and faces). Due to their high concentration of organic substances and high nitrogen content it may not be drained directly into the sewage system.
How does the municipal wastewater treatment process work?
Step-by-step guide:
Firstly, wastewater is drained to the Wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) through the main sewer system. Strange things end up in the WWTPs, ranging from smaller things like wallets, plants, and watches to bigger things like mattresses and animals. Sometimes even gold ends up at the WWTPs.
Therefore mechanical separation of these objects is required. This is called preliminary treatment or rather pre-treatment.
The large objects in the wastewater are removed by bar screens. Bar screen consists of various screens to separate various objects. Coarse bar screen racks remove coarse matter like paper, textiles, wood, plastic materials. Medium bar screen racks remove smaller objects (e. g. sanitary articles) to avoid plugging of the plant. Fine bar screen racks reduce the content of the solids in the sludge. Water then flows through the gravel chamber where the flow of the water is slowed down so that grit settles out of the water. The grit is later disposed of at the dump.
The following step is called the primary treatment during which the wastewater flows into primary settling tanks. Water is driven towards the hopper at the base of the tank where the hopper arm moves around the edge of the tank at the velocity of 4 cm/s. Treated water heads towards the edge and the particulates, of higher sedimentation velocity than the flow velocity, settle at the bottom of the tank. The settled particulates form sludge and are transported to a digestion chamber for further treatment. By the end of this step, the contaminant levels are reduced to 60%.
The secondary treatment is a biological step where microorganisms degrade organic carbon and ammonia and assimilate phosphorus. This reduces a load of organic matter and nutrients in the water. The sludge generated in this process (i.e. microorganisms and organic matter) is pumped out and moved back to the primary settling tanks.
Water from secondary treatment flows through the sand filters and activated carbon filters to filter out all the particulate and dissolved compounds in water thereby producing clear service water.
The final step of wastewater treatment is the thorough inspection of service water. This ensures that the treated water has contaminants below the acceptable limit.
Sludge pumped out of the settling tanks is added to the digestion chamber where it is continuously mixed at a higher temperature. Biogas is produced during the digestion process which can be used as a fuel.
When sludge digestion reaches an optimal level the sludge is transferred to thickeners where it is smoothly agitated and interstitial water between the flocs is released. The sludge is compressed by gravity and the clear water rises up.
The digested and dewatered sludge is adequately dried out and ripened. It is either discarded at the dump or if complied with agricultural standards it can be used as fertilizers for crops.
Water Treatment Synopsis:
The aim of treating water is to remove unwanted substances and impurities like pathogens and pollutants thereby producing high quality, clear and tasty drinking water. This also ensures that the water stays consumable for a long time and poses no health risk.
The Treatment Process:
In a typical treatment process, preliminary treatment of raw water is performed to make the water fit for the treatment plant. Coagulation and flocculation are generally the primary treatment steps where the dissolved and suspended particles from the water are separated. Coagulation neutralizes the charges of the particles and forms a gelatinous mass to trap (or bridge) particles thus forming a mass large enough to settle or be trapped in the filter. Generally, alum or ferric salt is used for this purpose. Flocculation is gentle stirring or agitation to encourage the particles formed from coagulation to agglomerate into large masses called flocs which subsequently settle.
During the secondary treatment settled solids are removed by sedimentation. In this process, wastewater flows slowly through a tank allowing suspended particles that are heavier than water to settle to the bottom of the tank. From there, the solids are pumped to digesters for stabilization.
Tertiary treatment may involve clarification, filtration, and disinfection of secondary treated water depending on the desired final quality of water.
Effective Energy Management in Water Treatment:
Drinking water is mainly obtained by purifying groundwater and surface water. This is done through chemical and physical treatment. The type of treatment depends on the quality of the raw water and is determined by its constituents and the contaminants to be removed. The whole process is Energy consuming and thus represents one of the biggest cost factors. Our smart products, services, and solutions help you to achieve transparency in terms of energy demand and meaningfully reduce your costs.
We offer a complete vertically integrated range of services to assist our customers from project planning stage to the commissioning of the project. Our consulting services include:
- Counseling and expert advice on viability of the project.
- Project report and detailed project plan.
- Designing of project layout.
- Detailed technical specifications of various machines and other utilities required.
- Various options in machinery.
- Delivery of various machines to the project site.
- Installation, testing and commissioning of machines.
- Fine-tuning and commencement of commercial production.
- Post production counseling, market information and feedback.
